Compared with UHF, HF library system is currently the most mature and popular solution for library due to its high identification rate and less influence by environment. It is expected that by adopting RFID solutions the Vatican Library will be able to control misuse of its library and at the same time provide its users the best possible facilities and access to rare manuscripts. In the ensuing discussions we will see how RFID technology is recommended for library automation. RFID technology is not just RFID library tags and other library assets; RFID applications in libraries will provide a comprehensive route for enhancing all library services and upgrade operations for everyone concerned with the library.
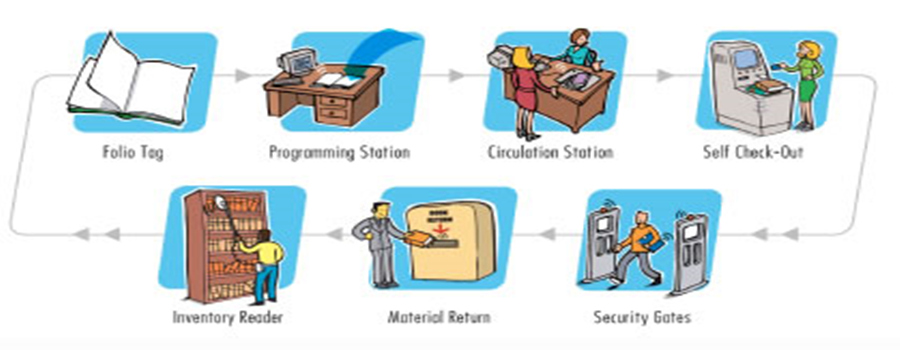
Issues: During a day, library managers have to supervise many activities within their libraries. If each of these functions is done by conventional methods, they will take time and lead to inefficiencies and unsatisfactory services to the library patrons. If by using RFID technology this process is made for time-efficient, then it could be recommended. Not only this, repetitive re-shelving task can be health risk to library staff. RFID tags contain a memory chip and RF antenna that can send and receive several bits of data.
Solution: For a library, smart labels have several added advantages over EAS and barcodes. One of the major benefits of an RFID system in a library is the ease of check-in and check-out of library items. Patrons can self check-in and check-out library items, saving themselves valuable time. After a check-out operation, the same RFID system disables the security requirements so that patrons can take the books, CDs, videos, etc. On-board receipt printer can print out the details of the items returned and automatically check items back to the library management system.
With hand held mobile digital library assistant and inventory wand, the library staff can obtain data about shelving the item and other information immediately (catalogue number, shelf number, etc.). Solution details: With RFID applications in libraries, all the library assets, namely books, manuscripts, CDS, DVDs, videos, audio cassettes, etc.