Uhf frequencies is the ITU designation for radio frequencies in the range between 300 MHz and 3 GHz, also known as the decimetre band as the wavelengths range from one meter to one decimetre.
Uhf frequencies is the ITU designation for radio frequencies in the range between 300 MHz and 3 GHz, also known as the decimetre band as the wavelengths range from one meter to one decimetre. Radio waves with frequencies above the UHF band fall into the SHF (super-high frequency) or microwave frequency range. Lower frequency signals fall into the VHF (very high frequency) or lower bands. UHF radio waves propagate mainly by line of sight; they are blocked by hills and large buildings although the transmission through building walls is strong enough for indoor reception. They are used for television broadcasting, cell phones, satellite communication including GPS, personal radio services including Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, walkie-talkies, cordless phones, and numerous other applications.
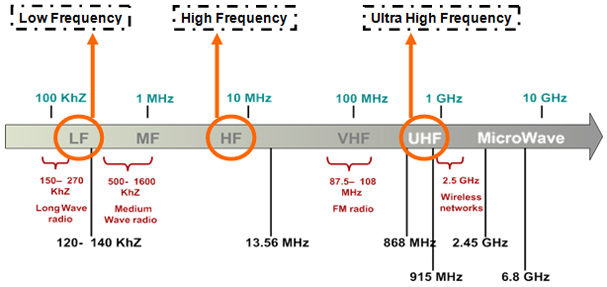
Most countries use 125 kHz or 134 kHz for low-frequency and 13.56 MHz for high-frequency RFID applications. Europe uses 868 MHz and US uses 915 MHz for Ultra-high frequency RFID applications. Some countries like Japan do not allow any use of the ultra-high frequency spectrum for RFID applications. To tackle this problem, some tag and reader manufacturers are providing devices that can work at more than one frequency.